Observe the following examples. In all of them there is the maximum number of non-cumulative double bonds, and there is also a ring atom linked to neighboring atoms only by single bonds. If that atom also has one (or two) hydrogen atoms, that hydrogen (or one of the two) receives the name of indicated hydrogen, and must be stated in the name.
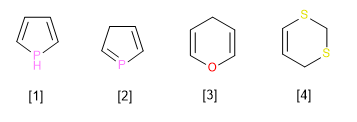
[1] A pyrrole heterocycle that has the largest possible double bonds, but lacks a double bond on the phosphorous atom. This fact must be indicated in the name through the hydrogen indicated in position 1. (1H-Pyrrole)
[2] Pyrrole heterocycle with the largest double bonds. The lack of double bond in position three should be reflected in the name (3H-Pyrrole)
[3] Pyrane heterocycle with hydrogen indicated in position 4. (4H-Pyrane)
[4] Dithiine heterocycle, with maximum double bonds, but with two saturated carbons that should be reflected in the name (2H,4H-1,3-dithiine)
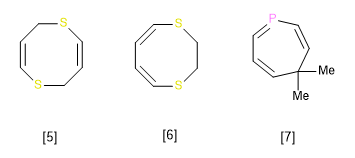
[5] Dithiozine heterocycle, with the maximum possible double bonds, but with saturated carbons in 2,6 positions that should be reflected in the name (2H,6H-1,5-Dithiozine)
[6] Dithiozine heterocycle missing a double bond between the 2,3 positions. (2,3-Dihydro-1,4-dithiozine)
[7] Phosphepine heterocycle, with the maximum possible double bonds. The saturated carbon of position 4 is indicated in the name. (4,4-Dimethyl-4H-phosphepine)