The Claisen condensation involves the reaction of esters in basic medium forming 3-ketoesters
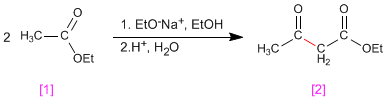
Mechanism:
Step 1. Formation of the ester enolate
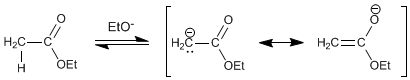
Step 2. Nucleophilic addition
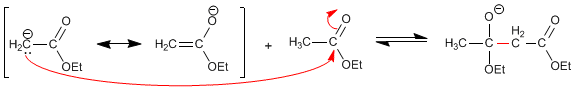
Stage 3. Ethoxide removal

The displacement of the equilibria is produced by the subtraction of the acid hydrogen in the final keto ester, forming an enolate that is protonated in the second stage.