acetyl chloride it is treated with diazomethane yielding the diazonium salt . chloride produced reacts with the diazonium salt to give the α-chloroketone . 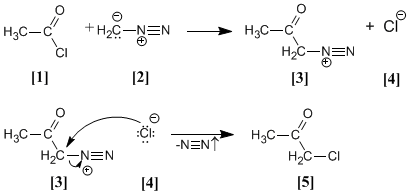
When two equivalents of diazomethane are used, the diazonium salt loses HCl to form the diazoketone. methyl chloride and nitrogen (N2 ). 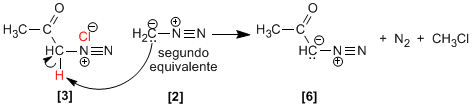
Diazoketone loses nitrogen to give a keto-carbene : 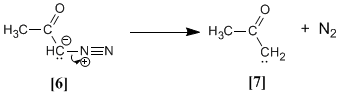
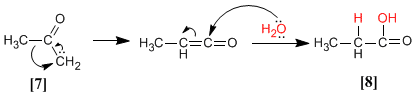
Keto-carbene can give the Wolff rearrangement, forming the carboxylic acid containing one more methylene group in its chain.