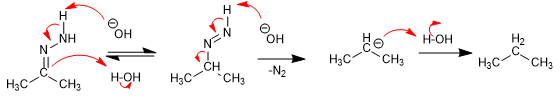
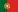
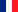
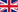
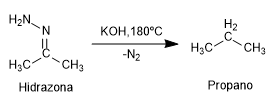
The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to alkanes via the corresponding hydrazone or semicarbazone under basic conditions and strong heating is called the Wolff-Kishner reduction.
The reaction is carried out in solvents with high boiling points 180-200°C (ethylene glycol). Substrates with ester and amide groups are hydrolyzed to the corresponding acids. Strongly hindered carbonyls are reduced more slowly. In the case of a,b-unsaturates, hydrazine condenses to give pyrazolidines.
Mechanism:
The mechanism of the reaction occurs with the deprotonation of the amino group of the hydrazone followed by the protonation of the carbon.