The Blanc reaction allows the chloromethylation of aromatic compounds.
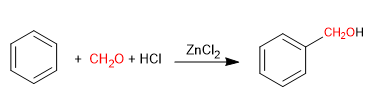
It uses as reagents methane with gaseous hydrogen chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid. The result is the introduction of a hydroxymethyl group on the aromatic ring (benzene) whose hydroxyl is replaced by chlorine in the presence of hydrogen chloride.
Mechanism:
Stage 1. Protonation of methanal
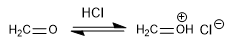
Stage 2. Nucleophilic attack of benzene to the electrophile.
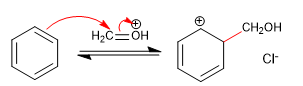
Stage 3. Recovery of aromaticity.
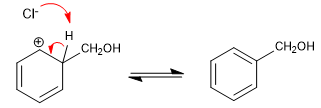
Stage 4. Substitution of hydroxyl by chlorine by means of SN1.
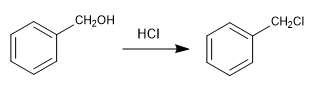
Chloromethylation can be used with aromatic compounds in general: benzene, naphthalene, anthracene. The benzyl chlorides obtained can be transformed into numerous derivatives: aldehydes, ketones, nitriles, organometallic reagents, etc.