Deprotonation of carbonyl compounds is an important method for generating enolates. An asymmetric dialkyl ketone can form two regioisomeric enolates in the deprotonation, and it is essential to know the conditions under which one of them is obtained predominantly.
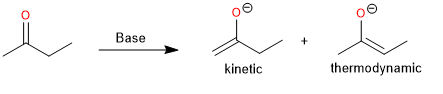
Although it may not be possible to direct the deprotonation to form exclusively one enolate instead of the other, experimental conditions can often be chosen that favor one of the regioisomers. The composition of a mixture of enolates can be governed by kinetic or thermodynamic factors. Kinetic control is exerted when the composition of the product is determined by the relative rates of the competing proton abstraction reactions. By choosing the experimental conditions appropriately, it is possible to establish both kinetic and thermodynamic control.
The conditions for kinetic control of enolate formation are those in which the deprotonation is rapid, quantitative, and irreversible.
Using a very strong base such as LDA or LiHMDS in an aprotic solvent.
Absence of excess ketone.
Lithium is a better counterion than sodium or potassium for the regioselective generation of the kinetic enolate, as it maintains a tighter coordination to the oxygen and reduces the rate of proton exchange.
The use of an aprotic solvent is essential because protic solvents allow equilibration of the enolate by reversible protonation-deprotonation, leading to the thermodynamically controlled enolate composition. Excess ketone also catalyzes equilibration by proton exchange.
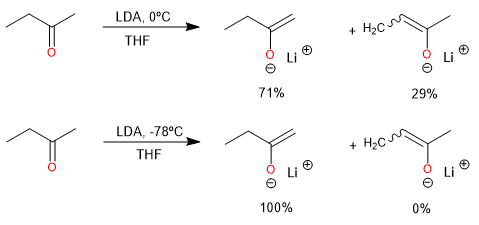
Low temperature favors the formation of the kinetic product.
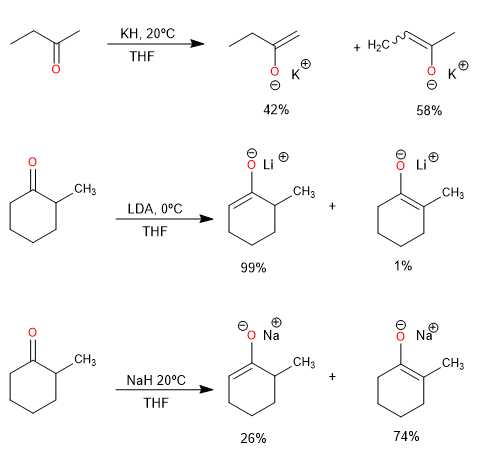
The lithium cation favors the formation of the kinetic product, while sodium and potassium produce a high percentage of the thermodynamic product.
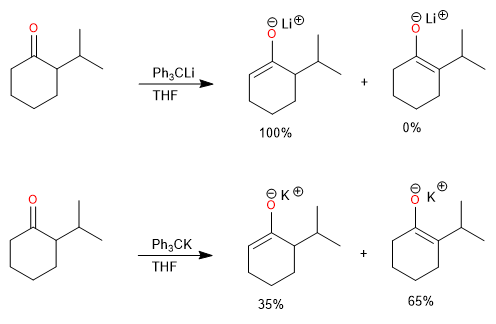
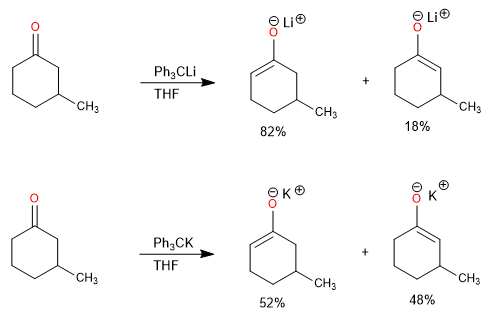
Steric hindrance at the alpha carbon also affects the ratio of kinetic and thermodynamic product.
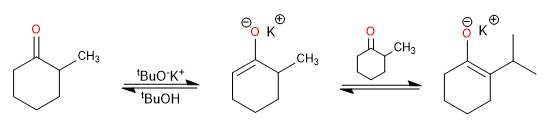
Alkyloxide-type bases, including tert-butoxide, yield mainly the thermodynamic product due to proton exchange between the ketone and the enolate.
The stereochemistry of enolates is a topic of great interest in organic synthesis, as the E and Z isomerism can affect the outcome of enolate reactions. Various factors, such as the deprotonating base, the presence of additives, and steric effects, can influence the E/Z selectivity of enolate formation.
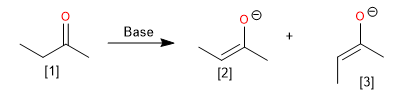
[1] 2-Butanone
[2] Z-enolate
[3] E-Enolate
In particular, the deprotonation of 2-pentanone with LDA in THF and HMPA results in different E/Z ratios for the deprotonation of C(3). The presence of HMPA (hexamethylphosphoramide) favors the formation of Z enolate, while LDA alone favors the E enolate. This behavior is attributed to the solvation of the Li+ ion by HMPA, which reduces the importance of Li+ coordination with the carbonyl oxygen and allows an acyclic transition state that favors the Z enolate.
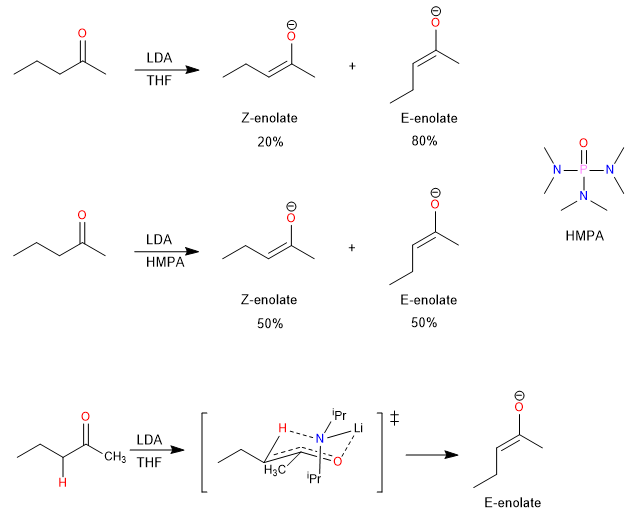
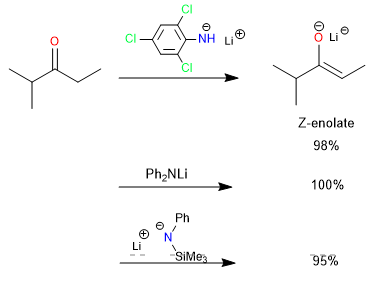
Other studies have shown that certain bases, such as lithium 2,4,6-trichloroanilide, lithium diphenylamide, and lithium phenyltrimethylsilylamide, exhibit high Z selectivity in enolate formation. This selectivity is associated with a lower basicity of the amide anion and an acyclic transition state that reduces steric effects.
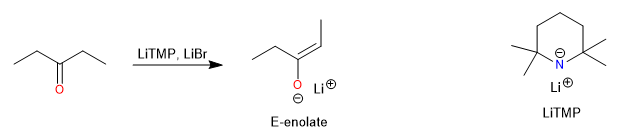
The addition of lithium halides, such as LiBr, can also affect the E/Z selectivity. In the case of 3-pentanone, the E/Z ratio can be improved from 10:1 to 60:1 by the addition of one equivalent of LiBr in the deprotonation with LiTMP (tetramethylpiperidinium lithium). NMR studies have shown that the addition of the halides leads to the formation of 1:1 mixed aggregates, but the exact mechanism by which this affects the stereochemistry has not yet been elucidated.
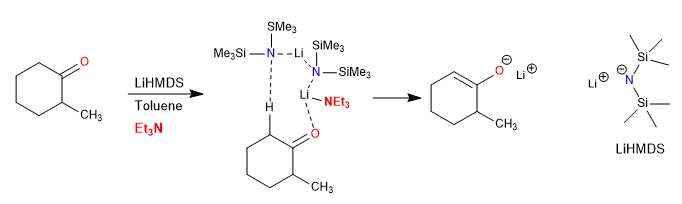
The inclusion of triethylamine in enolate-forming reactions in toluene leads to a significant acceleration in the rate of deprotonation of 2-methylcyclohexanone. This rate enhancement is attributed to a transition state that contains a dimer of LiHMDS [bis(trimethylsilyl)amide of lithium] and triethylamine. Steric effects in the amine are crucial for the selective stabilization of the transition state and the degree of acceleration that is observed.