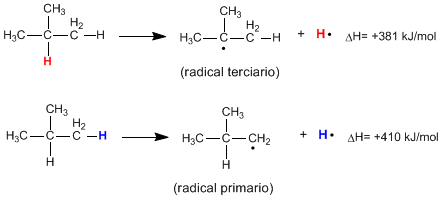
Homolytic breaking of the CH bond of an alkane produces alkyl radicals and free hydrogen atoms. The energy necessary for this breakage to occur is called dissociation energy and it is lower the more stable the radical formed is.
As can be seen from the following reactions, the energy required to break a primary CH bond is much higher than that required to break a tertiary CH bond.
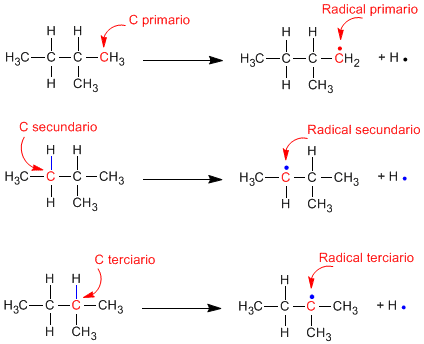
It is observed that the tertiary radicals are more stable than the secondary ones and these in turn more stable than the primary ones.
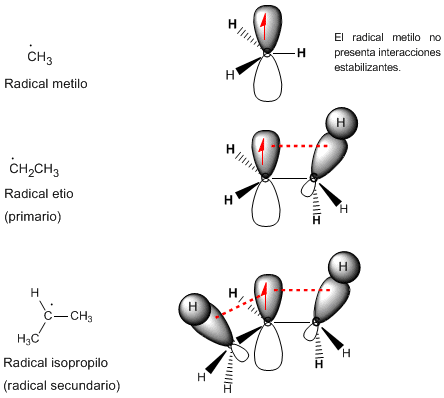
hyperconjugation
The phenomenon that stabilizes the radicals is known as hyperconjugation and consists of the interaction between the CH bond of the methyl group and the p orbital that has the unpaired electron. This interaction allows the pair of electrons from the bonding sigma orbital to relocate to the partially occupied p orbital, stabilizing it.