The formation of the allylic carbocation, stabilized by resonance, allows the reaction to evolve in two ways that lead to the kinetic and thermodynamic products.
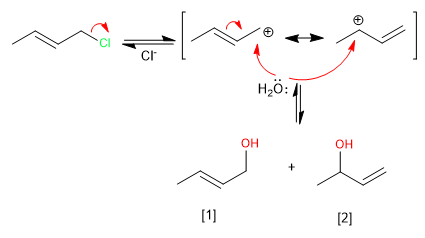
The kinetic product [2] is the least stable (terminal double bond), it is obtained at low temperatures and short reaction times.
The thermodynamic product [1] is the most stable (internal double bond), it is obtained at high temperatures and long reaction times.
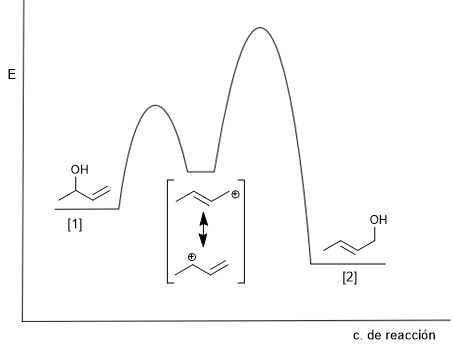
The attack of water on the more stable structure of the carbocation (below) gives rise to the kinetic product. The formation of this product is favored by low temperatures and short reaction times.
Attack on the less stable structure (above) gives rise to the thermodynamic product. This product is mainly obtained by working at high temperature and long reaction times.